 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
SLR Telescope Optical Layout |

 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
SLR Telescope Optical Layout |

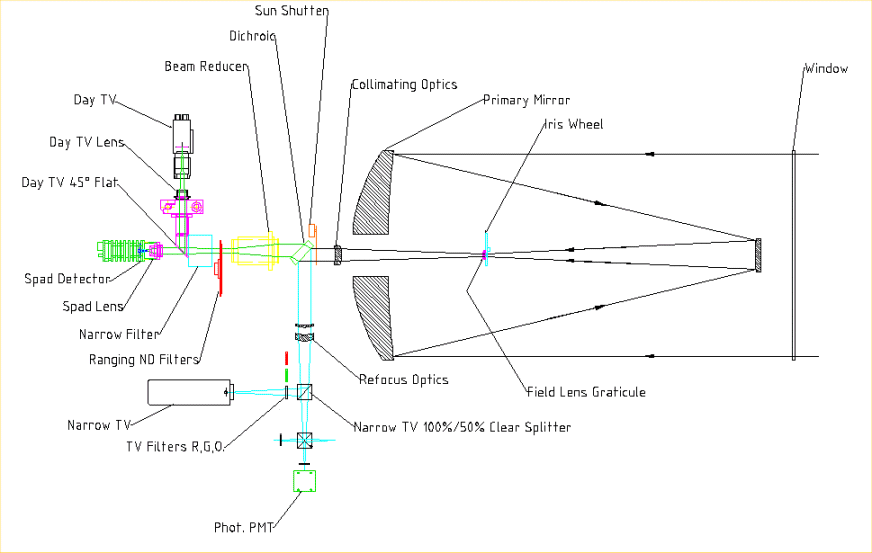
Dichroic
The dichroic splits the light from the telescope. Only the green light passes through and reaches the detector. The rest is reflected off the surface and sent to the Narrow angle camera. The dichroic is not 100% efficient and some green light is reflected, which allows the laser beam to be seen in the Narrow camera.Iris
A wheel rotates a selection of 5 Iris widths to increase or decrease the amount of light reaching the detector. Maximum iris field of view is 250 arcseconds, minimum is 20 arcseconds. The standard field of view used in the day is 48 arcseconds and the standard used at night is 84 arcseconds.Narrow/Daytime Filter
This filter removes the daytime noise and allows only light of wavelength matching the laser to pass through. FWHM =0.17 nm centred at 532.1nm. FWHM co-ordinates 532.027nm to 532.166nm. Peak Transmission is 57.10%. Figures quoted at ambient temperature of 35.0 degrees centigrade Part no. ANDV4781 from hereND Filters
The ND Filter is a disc around which Neutral Density increases from 0 to 4. The control system rotates this wheel automatically to increase or decrease the light reaching the detector. From target to target and depending upon the transparency of the sky, the return signal will vary from single photons to many. The ND Filter maintains a constant return signal and allows single-photon observing.Red/Green Filters
The light to the daytime camera passes through the red filter to allow daytime star pointing. This enables stars of third magnitude or lower to be seen. On a good day more than 40 stars positions may be recorded. Daytime pointing will not go within 45 degrees of the Sun. Even a few recorded star positions will provided the observer with offset suggestions. Using the green filter allows dusk and dawn viewing of the laser beam.Narrow angle Camera
The Narrow camera receives the light that has travelled through the iris. The satellite and laser beam can be seen and aligned. Click HERE to see an example of an image from the Narrow angle camera.Daytime Camera
The beam can be moved in the xy plane to achieve the best alignment. Click HERE to see an example of an image from the Daytime Camera.
| Go back to Research and Development
Page Go back to SGF main page |
Jump to site tour |  |
 |