
|

|

|
 |
 |
|
Gravimetry Analysis |

|

|

|
 |
 |
|
Gravimetry Analysis |
| Since October 2006 the SGF has been running in the facility basement an FG5 Absolute Gravimeter supplied by Micro-g Lacoste. The gravimeter is currently being operated to determine a midweek average value of gravity which can be found to an accuracy of ± 2 µGal. This routine observational programme will build up a long time series of local gravity at this important co-located site. The FG5 Absolute Gravimeter works by laser tracking a test mass free falling under gravity in a vacuum. The base of the dropping chamber is decoupled from vibrations from the outside world by a sophisticated "super-spring". This provides an absolute measurement of gravity. An 'experiment' consists of hourly sets of drops that are combined to give an average value of the local gravitational acceleration along with an error estimate. Both the average value and its RMS can be affected by local weather conditions, high wind in the nearby trees, weather systems over the Atlantic and earthquakes. A critical factor in the set up of the gravimeter experiment is the verticality of the tracking laser. The verticality is checked and adjusted before, during and after each experiment to get the best possible results. A poorly-set verticality will result in a low gravity reading. |
|
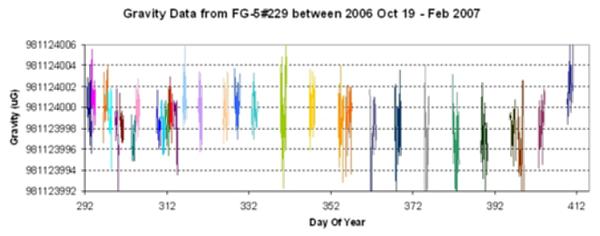 Preliminary time series of absolute gravity values at SGF, Herstmonceux. The first few months of measurements show local gravity variations of a few µGal about a mean of approximately 981124000µGal |
|
 |
|
|
(Wind Speed measured in knots) |
|
|
|
|
| Go back to SGF main page | |